Excel Function – SUBTOTAL
Excel Function SUBTOTAL
Excel Function “Subtotal” is most commonly used formula in excel and it can make your work easy while performing simple mathematical calculations because of variety of features like:
– You can use this function for different purposes instead of multiple functions i.e. SUM, AVERAGE, COUNT, MAX, MIN, Standard Deviation etc.
– It can help you to ignore values in filtered range or hidden values
In short this function is “ONE FORMULA FOR MANY”. Let’s learn this formula in detail
Excel Function SUBTOTAL Syntax:
Below are the Subtotal Formula syntax commonly used in Excel:
=SUBTOTAL(Function_num, Ref1,..)
1. =SUBTOTAL(9,Excel Range) >> Here 9 is used for SUM function2. =SUBTOTAL(1,Excel Range) >> Here 1 is used for Average Function3. =SUBTOTAL(4,Excel Range) >> Here 4 is used for MAX function Parameters:
– Function_num: It denotes the function number like 9 is used for SUM function. Though once you write Subtotal formula in excel, you will get the screen tip however you may refer the next section for detailed function numbers which you may use for various purposes
– Ref1,Ref2…: It is basically a excel data range where your value exists. You may write Excel Cells or Excel range i.e. A2,A3,A4 or A2:A4 respectively
Function Number For Subtotal Formula
There are two types of number you will find while writing SUBTOTAL formula
– Single Digit: 1,2,3,4 etc.
– Three Digit: 101,102,103,104 etc.
But if you see these number screen tips, you will realize that these are using the same function. Ever wondered why. Here is the reason:
– Single digit function number includes all values listed in the range for selected calculation including hidden cells, however consider only visible values in filtered list
– Three digit function number includes only visible values listed in the range for selected calculation and avoids hidden cells irrespective of filtered list or hidden rows
So three digit function number is more useful than Single digit number. Here you go for detailed listing:
So you should use Function_number as per your requirement and select the range. That’s all you need to do wtih this.
Things To Remember
– 1 digit function number includes all the numbers given in an Excel Range and works fine with filtered list
– 3 digit function number includes all the numbers given in an Excel Range and does not calculate hidden, filtered list
– It is suggested that SUBTOTAL should be used only in Vertical Ranges because if you use this function in a horizontal ranges, it will not exclude any hidden range values
How to use SUBTOTAL function in Excel?
-
See below image: you may write in a cell "=Subtotal("Type Desired Calculation Number","Select Range")
Filtered Range Results
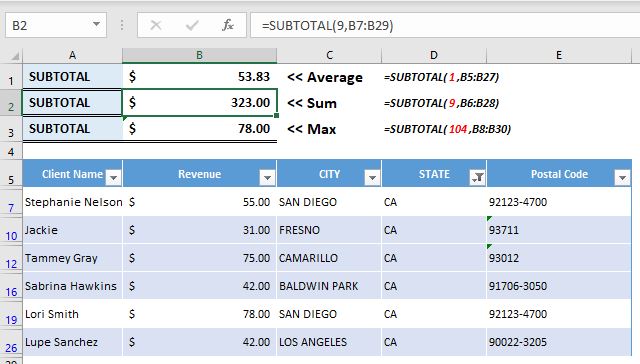
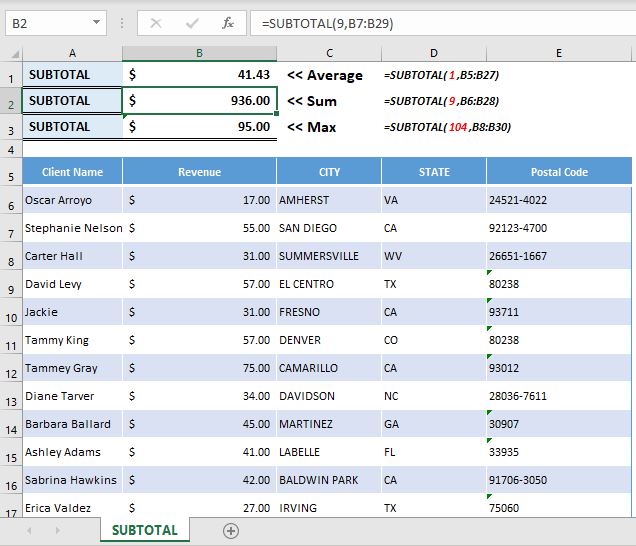
- Results Without Filter
Download Practice File
Hope you understood the concept now and can see the difference in above two images. Please comment below for any questions and yes do not forget to subscribe us.
Happy Reading 🙂