In Excel, the “MODE” function is a statistical tool that identifies and returns the most frequently occurring value within a set of numbers provided.
=MODE(number1, [number2], ... )
In Excel, the “MODEIF” function is a custom calculation that allows you to find the most frequently occurring value (mode) within a set of data, but only considering values that meet a specific condition specified in the formula
=MODEIF(data_range, criteria_range, criteria)
Click on any cell below to start practicing MODEIF Function. Check Instruction how to use the MODEIF Function.
=MODE(IF($A$2:$A$49=E9,C2:C49))
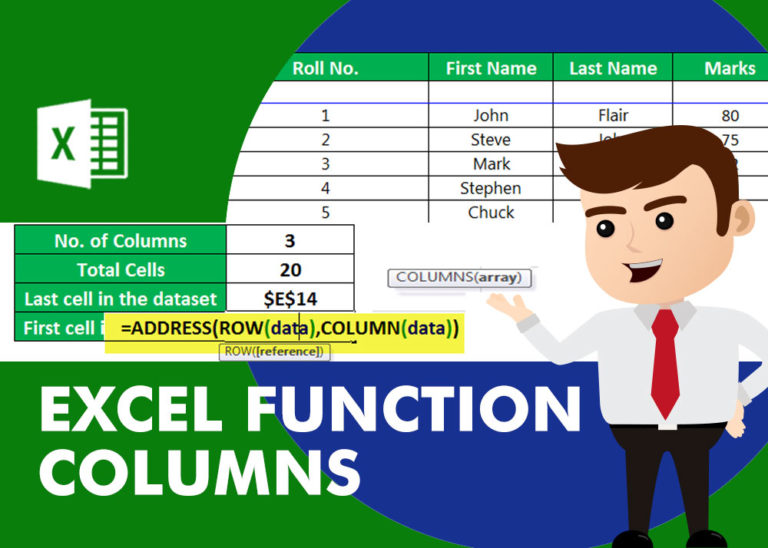
COLUMNS function is used to get the total count of columns in an array or in cells range for excel worksheet.

https://youtu.be/HmJL_y93pAs WEEKNUM function helps to calculate the week number of the given date in a year. It considers 1st January as first week by default and through the output for the given input date. Syntax:…
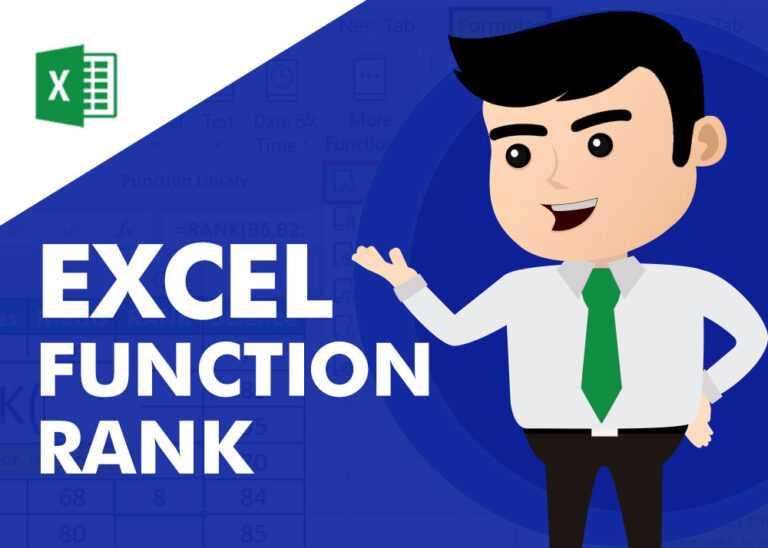
RANK function performs the Ranking in a range or list of numbers. Function returns the rank position and can assigned as highest or lowest value as 1st Rank
This tutorial explains how the TRANSPOSE function works and shows you the right way to use it to switch data in Excel.
Everyone has different preferences, even for work habits. Some people like to arrange data in vertical columns, while others prefer horizontal rows. If you ever need to switch the direction of your data quickly, the TRANSPOSE function can help
Understand how to find median in Excel with simple steps. Understanding the middle value in a set of numbers, known as the median, is important in the data industry. Professionals often use Microsoft Excel to calculate this. Excel’s MEDIAN function helps quickly find this value from long lists of numbers. This saves time and allows for further calculations using the median value. In this article, we explain what the MEDIAN function in Excel does, why it’s useful, and two methods to find the median in your data.
This tutorial explains how to use the IFERROR function in Excel to catch and handle errors. It shows you how to replace errors with a blank cell, a different value, or a custom message. You’ll also learn how to use IFERROR with functions like VLOOKUP and INDEX MATCH, and how it compares to other error-checking functions like IF ISERROR and IFNA