“NETWORKDAYS” function is very helpful feature in the Microsoft excel to calculate the working days from a particular period excluding “Saturday and Sundays”. NETWORKDAYS function subtract the Start Day from the End Date provided.
It comes with an advantage of excluding “Holidays” i.e. Holidays will not be counted as working days even those are falling between Monday to Friday.
This function really helps to in multiple ways, for example to calculate total pay days, prepare day wise work schedule, allocation and planning of project for an organization for a period. “Holiday” feature also helps to utilize the function in very effective manner.
Things To Remember
Please note that it will always returns to the whole number or integer value as output.
Also, Microsoft Excel calculate dates from 1st January 1900, if you use any date before than 1st January 1900 it will be shown as #VALUE! (Error)
Syntax: =NETWORKDAYS(start_date, end_date, [holidays])
Start_date argument is the date from which workday will be calculated. This date can be a working day or weekend, past day or future day.
End_date argument is the date to which workday will be calculated.
[holidays] Argument (Optional), Holidays argument is optional argument and used to excludes the holidays from NETWORKDAYS function output. We can give the complete range to exclude such days. Holidays are exception dates and such dates will not be counted as workdays (even those are falling on Monday to Friday)
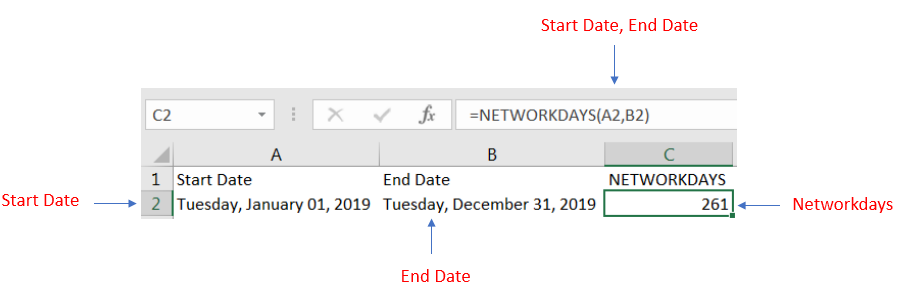
We have taken 1st January 2019 as Start date and 31st December 2019 as End date and will be calculating net working days during a period of one year. Following the syntax, we have 261 net working days during that period
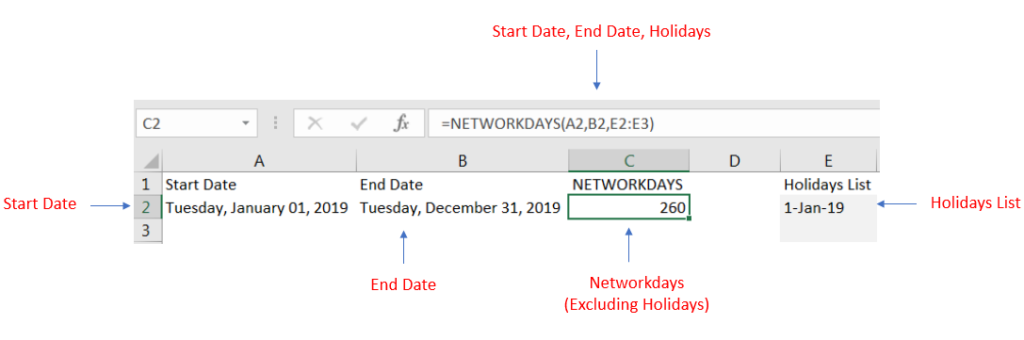
We have taken 1st January 2019 as Start date and 31st December 2019 as End date and have a list of holidays.
Net working days will be calculating considering 1st Jan 2019 as Holiday and total net working days for a year will be 260.
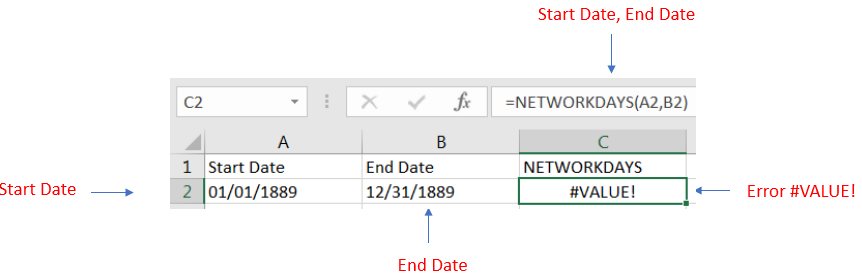
We mentioned that Microsoft Excel will calculate the date functions starting from 1st January 1900 and if we use any date prior 1st January 1900 this will show as #VALUE! (Error)
We have taken 1st January 1889 as Start date and 31st December 1889 and since it is prior to 1st January 1900 output is shown as #VALUE! (Error)

SEARCH function is used to find “position of character or text” in an available cell and this function is NOT case sensitive.

You must have faced a condition when your data cells contain extra spaces, leading spaces or trailing spaces and you wanted to remove these extra spaces to standardize the data. So here you may use…
Excel Function DATE When you work with dates in Excel, the DATE function is crucial to understand. The reason is that some other Excel functions may not always recognize dates when they are entered as…

In an “IF function” there will be two output i.e. TRUE or FALSE since either the statement will be “TRUE” or “FALSE”. If the statement is matching or correct, then output will be “TRUE” or if the statement is not matching or not correct then the output will be “FALSE
Excel Function- WORKDAY.INTL WORKDAY.INTL function is an advanced version of WORKDAY function with additional advantage of “Custom weekend options” For Example, with WORKDAY function weekends are treated as “Saturday and Sundays” however if you need…

https://youtu.be/HmJL_y93pAs WEEKNUM function helps to calculate the week number of the given date in a year. It considers 1st January as first week by default and through the output for the given input date. Syntax:…