=MAX(number1,[number2],...)
number1 argument is required argument where we can give range or value
[number2] argument is optional argument where we can give another range or value
To create a MAX formula in simple way, you have to type numbers directly in the list of arguments, like this:
=MAX(1, 2, 3)
In practice, it’s quite a rare case when numbers are “hardcoded”. For the most part, you will deal with ranges and cells.
The fastest way to build a Max formula that finds the highest value in a range is this:
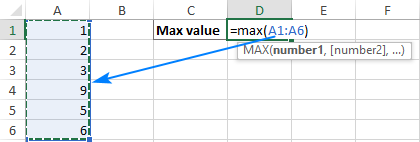
Decide where you want the maximum value to appear on your spreadsheet. This might be at the bottom of your data set, to the right or in any open cell. Click into the cell to select it.
Navigate to the “Home” tab on the ribbon. On the far right, you might see the sum symbol, which looks like a sigma. If you click the arrow to the right of the icon, it prompts a drop-down menu to open. Select “Max”.
The max function formula typically appears in the cell. You can then tell Excel which cell, array of cells or number to evaluate. You can do this by selecting a cell or range of cells or by manually typing in the arguments. You can then press “Enter”, prompting Excel to return the highest value.
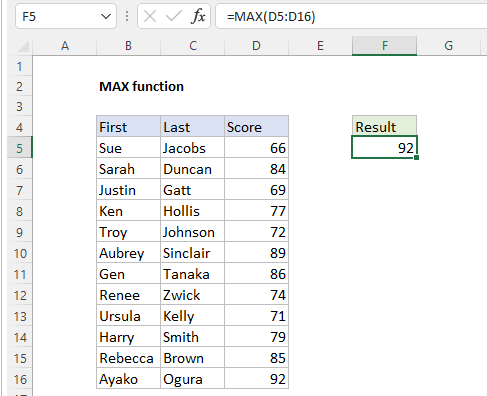
The MAX function returns the largest numeric value in the data provided. The MAX function can be used to return the largest value from any type of numeric data. For example, MAX can return the slowest time in a race, the latest date, the largest percentage, the highest temperature, or the top sales number.
The MAX function takes multiple arguments in the form number1, number2, number3, etc. up to 255 total. Arguments can be a hardcoded constant, a cell reference, or a range, in any combination. MAX ignores empty cells, text values, and the logical values TRUE and FALSE.
The MAX function returns the largest numeric value in supplied data:
=MAX(12,17,25,11,23) // returns 25
MAX ignores logical values and numbers entered as text, unless they are provided as arguments:
– Function will only consider numeric values while evaluating largest value
– Multiple ranges can be applied in function by separating them with comma (,)
– Text/ Spaces will be ignored by the function
– If No values in range or list of values (i.e. number argument) then output will return as 0 (zero)
Hope you learnt this Function,
Don’t forget to leave your valuable comments!
If you liked this article and want to learn more similar tricks, please Subscribe to us or follow us on Social Media by clicking the below buttons

Calculations With Date In Excel Dates function also be used to subtract the Year, Month and Days from the existing dates. Sometimes we need to subtract specific period from the date. In case you are…

Watch: How to use WORKDAY & WORKDAY.INTL Function in Excel? What is WORKDAY Function? The WORKDAY function in Excel calculates a date that is a specified number of working days before or after a given date. It…

This guide will show you quick and easy methods to find the number of days between dates in Excel.
Do you need to know how many days are between two dates? Maybe you want to find out the days between today and a date in the past or future, or just count the working days between two dates? Whatever you need, one of the examples below will help you find the solution
AVERAGEIF function is used to get the “average” of values for matching criteria across range. Average = Sum of all values / number of items.
This tutorial teaches the basics of correlation in Excel. It shows how to find a correlation coefficient, make a correlation matrix, and understand the results.
Correlation is one of the easiest calculations you can do in Excel. Even though it’s easy, it helps a lot in understanding how two or more things are related. Excel has all the tools you need to do a correlation analysis—you just need to know how to use them
How to use the compound interest formula in Excel and gives examples of how to calculate the future value of an investment with yearly, monthly, or daily interest. It also shows you step-by-step how to make your own Excel compound interest calculator.